On GPTs and Gems
Exploring how the Big 3 make it easy to design your own AI assistants, no programming required.
Hello there and welcome to another edition of Applying AI with Adam!
Today we’re exploring how you can tailor AI to your specific needs using tools like OpenAI GPTs, Google Gems and Anthropic Artifacts. These features let you build custom assistants, share them with others, and benefit from solutions that others create as well.
We’ll cover what these tools are, how to use them, some real-world examples, and suggestions to get started. Let’s dive in.
Beyond the Chat Window
Modern AI tools are evolving beyond back-and-forth chats (which are, of course, still amazing!). Increasingly, we’re seeing built-in agentic capabilities (like Researcher and GPT agents) take center stage. GPTs and Gems, launched back in 2023 and 2024 respectively, allows non-programmers to customize AI for specific needs (like drafting work emails or building mini apps) and share those creations with others.
They are a great entry point into AI automation and are well worth exploring regularly.
We’ll continue to focus on the Big 3 services, highlighting their out-of-the-box capabilities that anyone can start using. Think of them as a team of specialists embedded into your AI service that you can spin up and utilize as often as you’d like.
GPTs, Gems, and Artifacts: What’s the Difference?
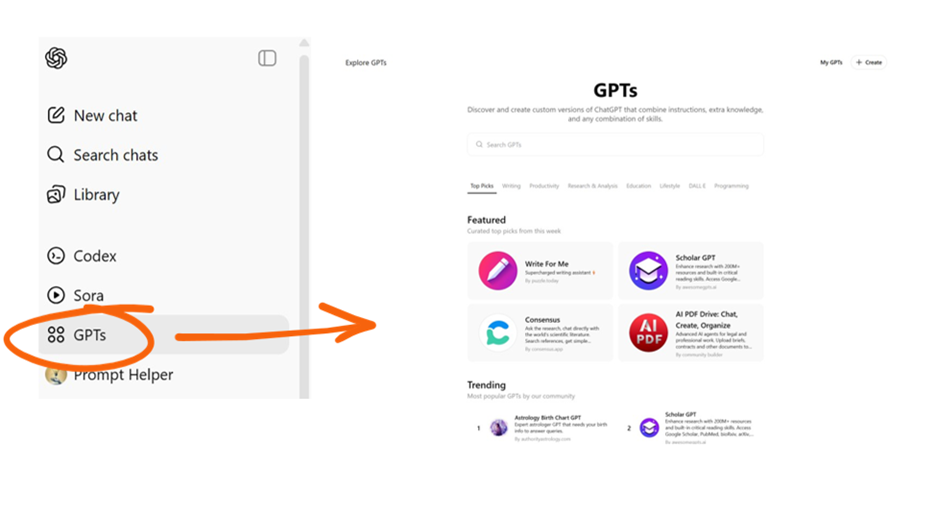
ChatGPT “GPTs” (OpenAI)
GPTs are custom versions of ChatGPT that anyone can create without programming or coding. Instead of typing the same prompt repeatedly, you can click your (or someone else’s) personalized GPT and jump right into a tailored experience.
What sets OpenAI apart is their impressive GPT Store (snapshot below). You can browse, use, and share community-built GPTs for thousands of use cases, along with plenty that OpenAI has developed as well. The store is refreshed regularly, and top-rated tools are surfaced for easy discovery. You could spend hours just searching for new ways to use AI and trying it out with a click of the button.
For more advanced users, GPTs also allow for technical flexibility. Among other things, GPTs can use OpenAI’s most advanced models, access the web, run Python code, and incorporate plugins, allowing them to perform advanced actions like adding calendar events or analyzing spreadsheets. You can give a GPT custom instructions, optional knowledge files, and enable tools (web browsing, code execution, etc.) to specialize it for a certain task.
Availability: Free-tier users can use some GPTs, but creating your own requires a Pro subscription ($20/month).
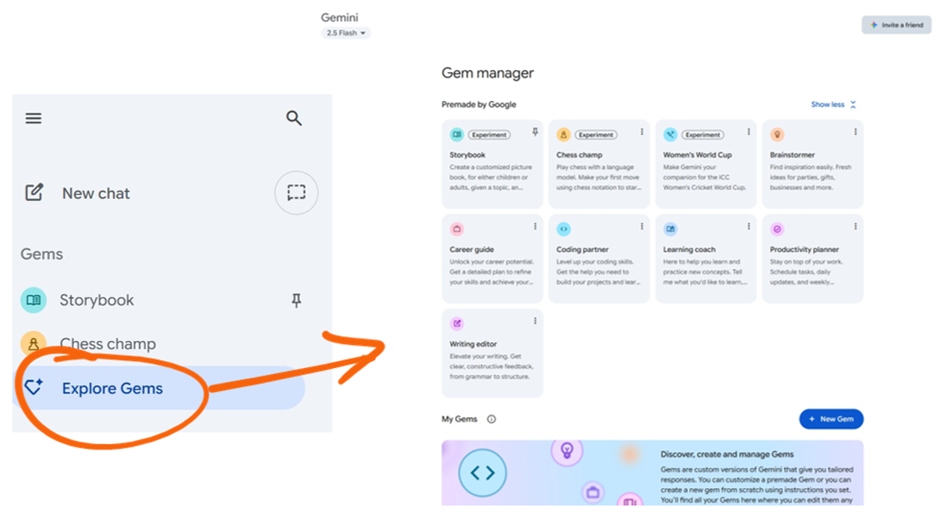
Gemini “Gems” (Google)
Gems are Google’s answer to GPTs. A Gem is essentially a reusable prompt with context that lives inside the Gemini AI app. You can create gems, use and reuse them, and also share them with others. It’s one of their most popular features and this guide might help you get started.
Like OpenAI, Google provides several premade Gems in their store (below) to start like Brainstormer, Career Guide, Coding Partner, Learning Coach, and Writing Editor, which are all very handy and useful. You can create and share Gems.
However, unlike OpenAI’s GPT Store, Gems are not publicly browsable. You can invite others to use/edit your Gem, yet there’s no central gallery to explore community-created options.
Availability: Gems are available to all users, but higher model access or advanced features may require paid plans.
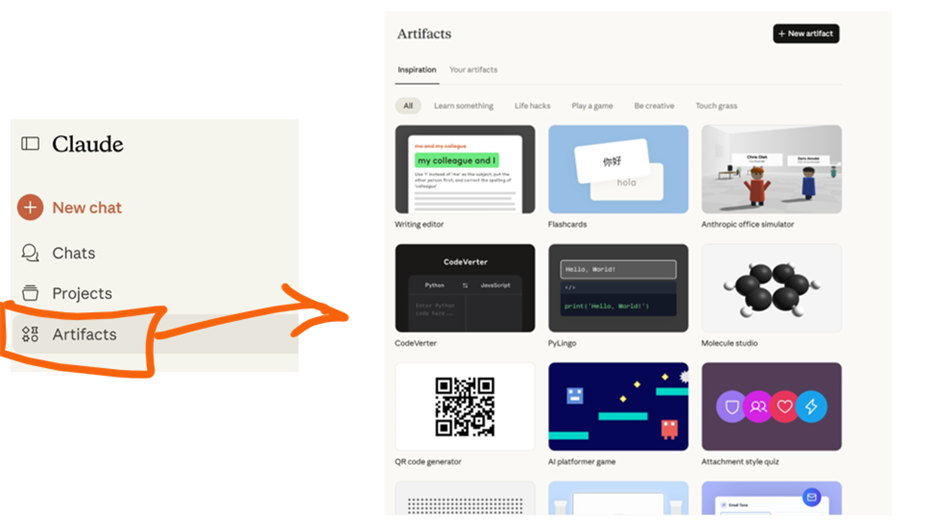
Claude “Artifacts” (Anthropic)
Artifacts are a distinct twist on AI assistants – they let you create interactive, shareable mini-applications or content within the Claude AI chat interface. While ChatGPT and Gemini output text (or images) into a chat, Claude can produce an Artifact: a separate window containing formatted text, live code previews, charts, or even working web apps. In June 2025, Claude upgraded these capabilities to support embedded AI capabilities, meaning the artifact itself can call an AI, like a mini app that calls Claude for additional answers. Pretty cool!
The key idea here is turning your chat into a creation: you describe what you want, and Claude builds a self-contained result that you can interact with, edit, and share.
Like Gemini, Claude doesn’t have a public “store” or browsable community gallery like OpenAI’s GPT Store, but any user can publish an Artifact and share it via link (and others can open and remix it).
Availability: Available to all Claude users (Free, Pro, and Team). Team plans support project-based sharing. All tiers are subject to usage caps..
I was thinking through how deep I should dive in here, but I’m going to leave it there. If you want to explore further, I thought this was a great 101 guide to learn more.
(Of course, all above info is as of September 2025. Features and access may change.)
What People Are Building
There are countless ways to put these tools to work. Browsing the GPT Store is one of the best ways to see what’s possible and discover community-built assistants that might inspire you. Below are a few more creative ideas from others to get the juices flowing:
Email Drafting – Want your AI to better capture your personal voice? One user copied and pasted a set of work emails into a text file, then gave GPT instructions to edit new drafts in their style. (Source)
Knowledge Base & Support GPT – A support engineer loaded product documentation and response templates into a GPT. The result: a “tech support bot” that helps troubleshoot issues, draft replies to customers, and even format internal escalation reports. (reddit.com).
Subject Tutors – Some use GPTs as on-demand teachers tailored to specific subjects. For instance, one user built a History Teacher GPT and a Math Teacher GPT, each loaded with textbook excerpts and notes. (reddit.com). (Also know that OpenAI also recently added their study mode – another post!)
Language Practice Partner – Learners have created GPTs as interactive conversation partners. For example, a “Spanish Conversation Coach” GPT can use custom glossaries or class notes to guide realistic practice dialogues.
Storytelling for Kids – One parent built a bedtime storytelling GPT with a simple framework: each tale starts and ends in a familiar way, but the middle is interactive. The GPT asks the child questions in a choose-your-own-adventure style. The child picks a theme (often “something spooky!”), and the GPT weaves a unique, age-appropriate story — sometimes with AI-generated illustrations.
Fiction Writing Assistant – Many authors build GPTs to help develop plots and characters. A novelist might upload bios and outlines, then instruct the GPT to act as a story development partner.
Tax and Finance Advisor – Some users build GPTs to help navigate repetitive but complex domains like taxes (with the caveat that outputs should always be verified). One example: a “Small Business Tax Advisor” GPT providing general LLC guidance.
Coding Partner (Gemini) – Google includes a premade Coding Partner Gem, but developers can customize it. One coder extended it with instructions like: “Use functional Python and always include unit tests.” Now their Gem consistently answers in their preferred style. (blog.google)
“Fridge Forager” Cooking Gem – A Googler built this playful Gem to suggest recipes based on what’s in her fridge. It takes into account her skill level and preferences, then recommends dishes tailored to the ingredients at hand. (blog.google).
Text and Data Converters (Artifacts) – A common Artifact use case is creating quick one-off utilities. For instance, a developer asked Claude to build an Artifact that escapes HTML characters and provides a “Copy to Clipboard” button. Claude generated a working HTML page instantly. (datacamp.com, simonwillison.net).
Games and Simulations (Artifacts) – People have even built simple games in minutes. In one case, two colleagues created a working checkers game via Claude Artifacts in under five minutes! (albato.com)
Case Study: From Prompt to Music
First off, if you read our previous post on prompting, you may remember Prompt Helper which I created. But let’s try something new…
There’s so much that you can explore and try out. Here’s one fun experiment that just took a few minutes to explore:
Looked through the top charts on the GPT Store and found Song Maker GPT
Clicking it started a chat, where I picked one of the suggested song options (a folk song about missing home)
It generated lyrics (screenshots below) and at the end of the chat it asked if I wanted to generate the music. So, I clicked.
That launched a new browser tab for a tool called Free AI Song Generator with my song lyrics preloaded.
Hit generate music, waited about 2min… and voila, AI generated folk music!
I’ve never made AI music before. This made it super easy, all packaged up for easy use for anyone who wants to try it out. Thanks, GPT Store!
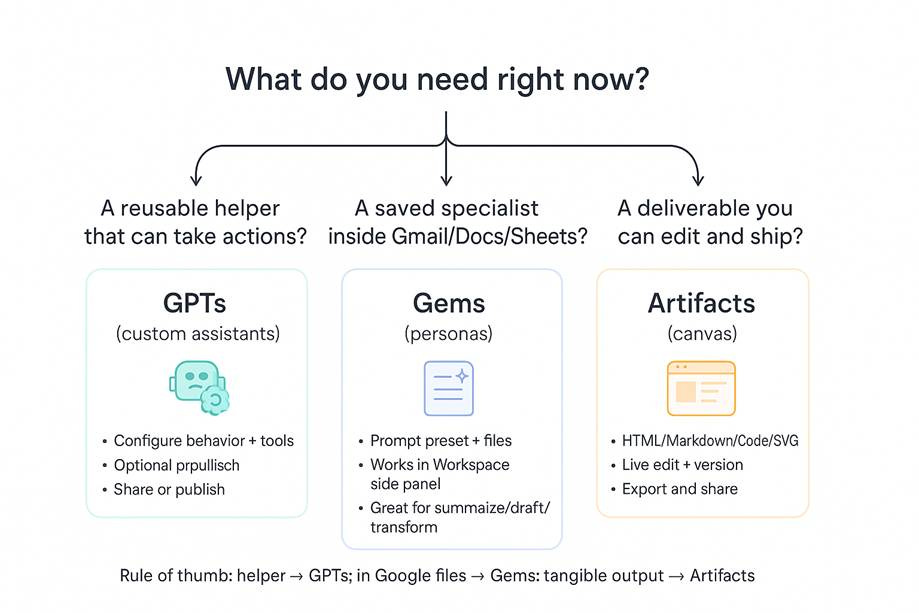
When to use what
How should you think about using these and do they work together? Obviously the first question is what service you use. Start there. But if you’re open or have multiple, below are a few suggestions on thinking about when to use each.
Need a reusable helper (especially if it involves actions or API calls)? GPTs
Want to explore GPTs from around the world? GPTs
Working in the Google ecosystem (Gmail/Docs/Sheets)? Gems
Want an interactive deliverable? Artifacts
I asked GPT to draw me a decision diagram, this seems largely about right to me…
Getting Started with Your Custom AI
Start by exploring the pre-built GPTs and Gems offered by OpenAI and Google. See what provides value for your workflow. Then, expand into the GPT Store or try creating something yourself.
Challenge: Try a new GPT or tool today and create something you’ve never built before. You might surprise yourself!